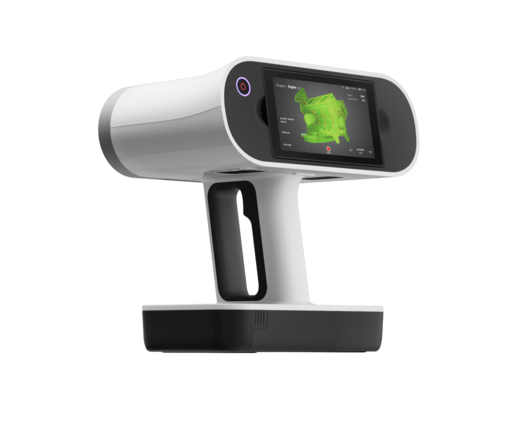
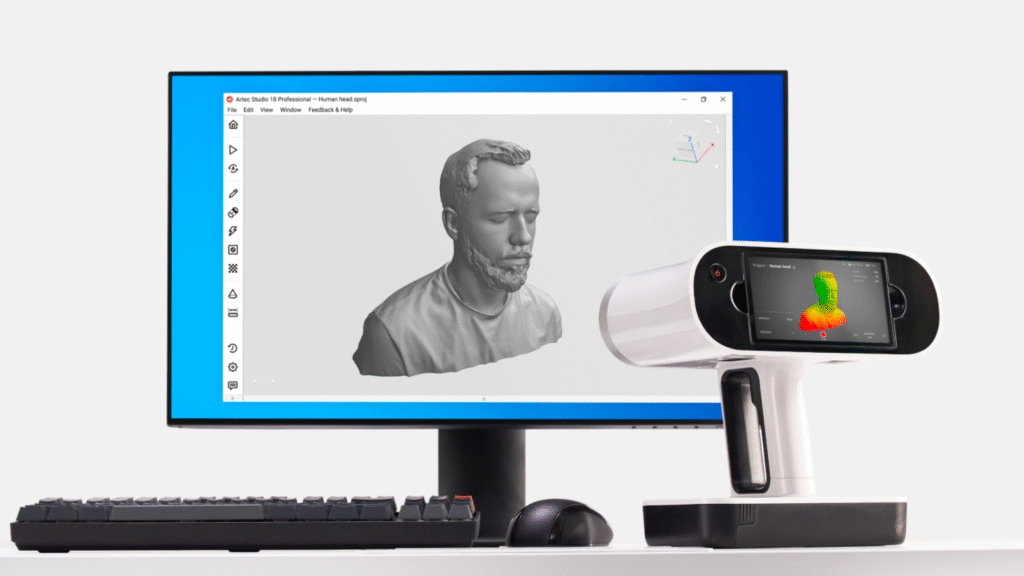
In today’s rapidly advancing world, precision, mobility, and efficiency are more important than ever. One innovation reshaping industries from engineering to healthcare is the handheld 3d scanner. These portable devices have revolutionized the way professionals capture, analyze, and digitally reproduce real-world objects.
Unlike bulky stationary systems, a handheld 3d scanner offers unmatched mobility, allowing users to scan objects in studios, construction sites, museums, hospitals, and outdoor environments. Whether you’re reverse engineering a machine part or digitally preserving an ancient artifact, handheld scanners make 3D capture more accessible and practical.
How Handheld 3D Scanners Work
A handheld 3d scanner maps an object’s surface by capturing millions of measurement points and converting them into a 3D model. Instead of requiring fixed setups, users freely move around the object, capturing hard-to-reach details.
The main technologies include:
Structured Light Scanning
Projects patterned light onto an object. Distortions in the pattern help calculate accurate geometry.
Laser Triangulation
Uses laser beams and sensors to measure the distance from the scanner to the object’s surface.
Infrared Depth Sensing
Ideal for scanning faces, bodies, or delicate objects. Safe, fast, and accurate even on organic shapes.
The output is a detailed 3D mesh, ready for editing, rendering, analysis, or 3D printing.
Why Handheld 3D Scanners Are Becoming Essential
1. Portability That Saves Time
Their lightweight, compact designs allow users to scan on the spot—no need to bring objects into a lab or studio.
2. High Accuracy and Detail
Modern handheld systems can capture micron-level precision, suitable for engineering, medical modeling, and quality inspection.
3. Easy and Intuitive
With simplified interfaces and wireless connectivity, even beginners can learn scanning quickly.
4. Speed and Project Efficiency
Scanning that once took hours can now take minutes, speeding up workflows across industries.
5. Affordable and Accessible
More cost-effective than traditional systems—perfect for startups, artists, educators, and freelancers.
Industries Using Handheld 3D Scanners
Engineering & Product Design
Engineers use handheld scanners for:
- Reverse engineering
- Rapid prototyping
- Quality inspection
- Component alignment and verification
They allow designers to digitize physical parts, refine models, and build prototypes faster.
Healthcare & Medical Modeling
Handheld scanners support:
- Prosthetics
- Orthotics
- Dental impressions
- Surgical planning
- Facial reconstruction
Accurate patient-specific data leads to better comfort and medical outcomes.
Art, Restoration & Cultural Preservation
Museums and archaeologists use handheld scanners to:
- Digitally preserve artifacts
- Recreate damaged elements
- Safely document fragile items in the field
Perfect for preserving historical treasures without risk of damage.
Education & Research
Students gain hands-on experience using handheld scanners in:
- Engineering labs
- Art and design classes
- Medical training
- Archaeological research
Scanning real objects enhances learning and experimentation.
Animation, Gaming & Film
Used for:
- Facial capture
- Prop modeling
- CGI visual effects
- Environment scanning
They drastically reduce production time while improving realism.
Handheld vs. Stationary 3D Scanners
When Handheld Is Better
- On-site scanning
- Complex organic shapes
- Confined spaces
- Human body scanning
- Outdoor environments
When Stationary Scanners Win
- Ultra-high precision inspections
- Full automation
- Very large and complex industrial parts
Professionals often choose handheld for flexibility and real-world versatility.
How to Choose the Right Handheld 3D Scanner
Consider:
- Required accuracy and resolution
- Object size
- Speed and frame rate
- Software tools
- Wireless vs. wired
- Budget
Many professionals prefer a reliable handheld 3d scanner model capable of fast, high-quality capture suitable for both simple and advanced projects.
The Future of Handheld 3D Scanning
AI-Powered Scanning
AI will help clean scans, fill gaps, and generate perfect meshes automatically.
Faster and More Accurate Sensors
Speed, detail, and color capture will significantly improve.
AR/VR Integration
Users will view and manipulate 3D models in mixed-reality environments.
Material Recognition
Future scanners will capture geometry and detect material type and texture.
Greater Affordability
As technology matures, handheld scanners will become common household tools.
Conclusion
From engineering and healthcare to art, education, and entertainment, the handheld 3d scanner is transforming how we interact with the physical world. Its accuracy, portability, and ease of use make it one of the most influential tools in modern digital capture.
As innovation continues, handheld scanners will only become more capable and essential—empowering professionals, creators, and learners with faster, smarter, and more accessible 3D technology.